The Debt Ceiling Crisis Resolves With a Compromise Between Republicans and Democrats
Wikimedia Commons. Licensed by CC0 1.0.
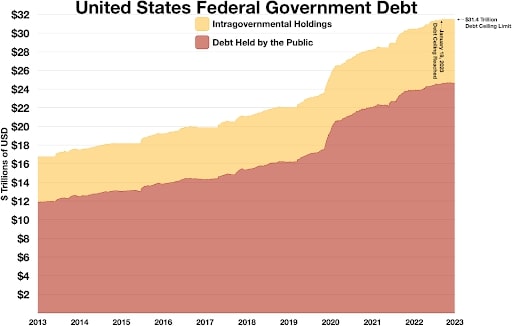
A graph shows the gradual build-up of debt in trillions of dollars since 2013. The debt ceiling was created in 1939 by Congress and was reached for the first time in 1953.
During May and early June, the U.S. government struggled with an impending problem: the debt ceiling. Congress had to decide to either raise the debt ceiling or let the economy crash harder than ever before. A bill was passed to raise the debt ceiling last week on Wednesday, May 30, just before the deadline on June 5.
Senior Ethan Bohnert, a passionate economics student, reveals what the debt ceiling is.
“The debt ceiling is an artificial limit that Congress sets to our government for the amount of debt that it can accrue,” explained Bohnert.
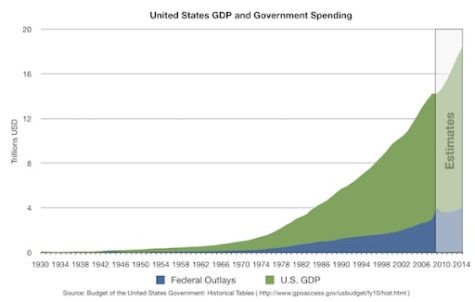
In order to pay for the many projects, systems and agencies throughout the country, the government needs more money than what taxes bring in. That is where the country’s interest and debt come from.
“The government spends money on lots of different things, and how the government funds that is through collection activities like taxes. And then they borrow money,” clarified Clark Avery, the macroeconomics teacher at Sage Creek High School.
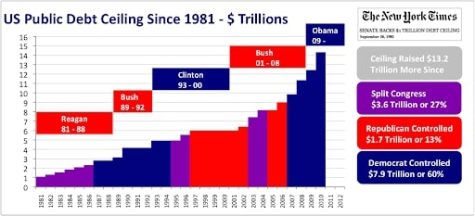
Furthermore, the problem is the continuously growing pile of debt that the government creates and doesn’t pay back. Avery defines this phenomenon in his own terms.
“The government in the long term has been borrowing less, or spending more than we make, every year, after year, after year,” Avery continues, “and that difference is known as a deficit.“
Because of the United States’ standing in the world’s financial scheme as one of the most prominent countries, a collapse could have disastrous consequences. Due to the backlog of debt, Congress must decide to either raise the limit or lower the value of the United States dollar.
“The effects of the U.S. hitting the debt ceiling with no extension is so horrific that an agreement that extends the ceiling was going to happen regardless of whatever the news was going to say,” claimed Bohnert. “If the debt ceiling wasn’t raised, the U.S. would stop printing new bonds to be sold, which would dramatically hit the value of the U.S. dollar.”
This would become a global issue because of the standing of the U.S. dollar. The dollar is the world’s reserve currency, so the entire world relies on its value.
According to Bohnert, “If the dollar lost a lot of its value, we would see the Great Depression times a hundred on a global scale.”
The new bill passed to raise the debt ceiling was a compromise between the Republican and Democratic parties, resulting in a few budget cuts for government programs. Bohnert explains one of the facets of the bill, the stop of the student debt freeze.
“Basically the student debt freeze was the government paying for the interest of many university students’ school loans instead of the students paying for it themselves, which would reduce the individuals’ monthly payments,” Bohnert says.
Another part of the bill reduces eligibility for SNAP, so select people will need to work more to receive aid. SNAP, or Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, provides low-income families with food benefits to receive food that may not be within their budget.
“Expanding work requirements for the SNAP program, it’s what used to be known as food stamps,” Avery explains. “Most able-bodied adults between 18 and 49 will have to put in some documented higher level of work to be able to be eligible for the benefit.”
Another section of the deal pulls back all leftover money from Covid-19 aid from families that needed assistance during the pandemic. The governmental aid was an economic relief program for families that struggled with unemployment.
“It takes any of the Covid money that was authorized back in 2020, 2021 and 2022- Covid aid. Any of it that hasn’t been spent is clawed back,” Avery explains.
While this situation may seem scary, Bohnert encourages everyone to keep an open mind and remain positive.
“This isn’t a new thing though. Trails and recessions have been happening ever since the country started, and so it will sound hard certainly, but at the end of the day we will make it through like we always do,” said Bohnert.